Introduction
Tree topology is a hybrid network topology that combines elements of both bus and star topologies. It features a hierarchical structure, resembling a tree with its branches, where nodes are connected to a central backbone through intermediate hubs or switches. This topology is widely used in large networks that require scalability, structured management, and hierarchical data flow.
What is Tree Topology?
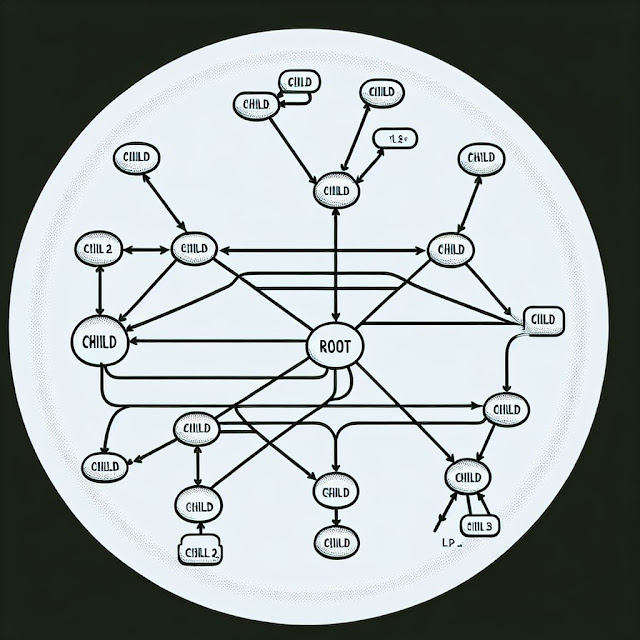
Tree topology is a network structure where nodes are organized hierarchically. It consists of a root node connected to intermediate nodes, which further connect to leaf nodes. The root node is typically a central hub or switch, with each level of nodes branching out like a tree. This design allows for efficient data transmission and network management.Why is Tree Topology Used?
Tree topology is used for its scalability, hierarchical management, and fault isolation. It allows for easy expansion by adding new branches, supports multiple devices, and provides structured data flow. The ability to isolate network issues to specific branches makes it ideal for large enterprises and educational institutions.Where is Tree Topology Used?
Tree topology is commonly used in:Enterprise Networks: Facilitates hierarchical management and departmental segmentation.
Educational Institutions: Ideal for connecting computer labs and administrative offices.
Wide Area Networks (WANs): Suitable for connecting multiple local area networks (LANs) over a large geographical area.
Data Centers: Organizes servers and networking devices into structured groups for better management.
How is Tree Topology Used?

Tree topology is implemented using a combination of switches, hubs, and cables. The root node connects to secondary hubs or switches, which further connect to end devices. Data flows hierarchically from the root to the leaf nodes, with network protocols like Ethernet and IP aiding in communication. Tree topology also supports VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) to manage data flow efficiently.
What is Used in Tree Topology?
Hubs and Switches: Central and intermediate devices for connectivity.Cabling: Ethernet cables, fiber optics, or wireless connections.
Network Interface Cards (NICs): Ensure devices connect to the network.
Routing and Switching Protocols: Manage data transmission.
Monitoring Tools: For managing and troubleshooting network performance.
What are Tree Topology?
Tree topology involves a multi-level structure with a clear hierarchy. The network is segmented into different layers, each playing a specific role in data distribution. The structure enhances network management by allowing specific segments to be isolated for maintenance or troubleshooting without impacting the entire network.Structure of Tree Topology
The tree topology structure consists of multiple levels:Root Node: The topmost node, usually a powerful switch or hub.
Intermediate Nodes: Connect the root node to the leaf nodes, often using secondary hubs or switches.
Leaf Nodes: End devices such as computers, printers, and other networked devices.
Branches: Connections that link different nodes in a hierarchical manner.
Backbone Cable: Acts as the main line connecting all segments.
Advantages of Tree Topology
Scalability: Easy to expand by adding more nodes to branches.Hierarchical Management: Supports structured data flow and network control.
Fault Isolation: Problems in one branch do not affect the entire network.
Flexibility: Combines the benefits of bus and star topologies.
Efficient Data Flow: Allows segmented network traffic management.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
High Cost: Requires a lot of cables and networking devices.Complex Configuration: Needs careful planning and management.
Dependency on Backbone: Failure of the main cable disrupts the network.
Maintenance Challenges: Troubleshooting can be difficult in large networks.
Single Point of Failure: The root node is critical for network functionality.
Real-World Implementations of Tree Topology
Corporate Networks: Segmenting departments in a large office.Educational Campuses: Connecting different buildings to a central server.
ISPs (Internet Service Providers): To structure regional network distribution.
Government Networks: Managing segmented network access across agencies.
Hospital Networks: Connecting different wards and administration units.
Advanced Insights and Emerging Trends in Tree Topology
Integration with Cloud Services: Hybrid networks connecting on-premises and cloud resources.
Support for Virtualization: Enhanced by VLANs and software-defined networking (SDN).
Use in IoT Networks: Helps manage data flow in smart buildings and smart cities.
Enhanced Security Protocols: Facilitates segmented security policies through hierarchical design.
Future Potential: Adapting to support advanced technologies like 5G and edge computing.
Conclusion
Tree topology offers a robust and flexible networking solution for large-scale environments that require hierarchical management and scalability. Its blend of bus and star topology features makes it suitable for enterprise, educational, and governmental networks. While it has certain limitations, its structured design and fault isolation capabilities often outweigh the drawbacks. As networking technology evolves, tree topology continues to play a vital role in modern network infrastructures.This comprehensive guide aims to provide a deep understanding of tree topology, including practical insights and advanced applications.

